With each edition of the Aware Force cybersecurity newsletter, employees are able to send comments, suggestions, and, most importantly, their cybersecurity questions.
Over the past 12 months, the most common cybersecurity question from employees involves “how to select a good password manager.”
40% of respondents to the newsletter’s Cybersecurity Q&A feature, asked whether they needed password management software, how to use it, whether it’s safe to use one, and what they should do following the security breach of the password management company LastPass.
While Aware Force does not recommend specific products, an analysis of trade publications and consumer technology sources ranks Dashlane, BitKeeper, Zoho, BitWarden, 1Password, and NordPass among the top choices for password managers.
Aware Force advises organizations to have a password policy covering access to any online assets. Whether accounts are used for testing, workstation setups, day-to-day use, or superuser/root privileges, establishing and maintaining a firm password management policy is the foundation of a secure organization.
Our answer: Most web browsers offer at least a rudimentary password manager. Dedicated password managers offer a more comprehensive solution for securing your online accounts. These managers provide enhanced security features like two-factor authentication, password strength analysis, and breach alerts. In addition, they are compatible with a wide range of devices and platforms, making them more versatile than their browser-based counterparts.
Therefore, you may need more than browser-based password managers to provide the level of security necessary to protect your company. Instead, using a dedicated password manager offers a more robust defense against potential cyber-attacks.
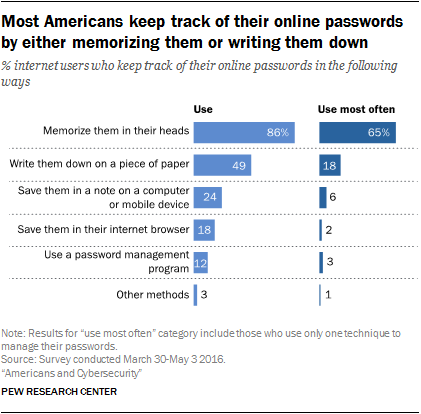
According to a study by Pew Research Center, only 12% of online adults say that they ever use password management software to keep track of their passwords. Another study by Panda Security found that just 15% of Americans use an online password manager. As for built-in browser password managers, according to the same Pew Research Center study mentioned earlier, 18% of online adults say they save their passwords using the built-in password-saving feature available in most modern browsers.

If you’re a fan of statistics, this might have your cyber sensors triggering all over the place: Google has released some data about passwords that should be concerning to organizations:
The Ponemon Institute also has companies’ perspective:
In short, we have a combination of populational bad habits and an organizational need for adequate systems to protect their data. The result: a feast for cybercriminals.
When selecting the right password manager for a company or personal use, it’s essential to consider these factors:
Reading user reviews and professional assessments from reputable sources can also help you make an informed decision.
In light of the LastPass security breach, users of any password manager should be cautious and follow best practices for online security:
In conclusion, password managers can significantly improve the security of your online accounts by generating and storing strong, unique passwords.
While browser-based password managers offer a basic level of protection, dedicated password managers offer a more comprehensive solution.
Ensure your personnel is informed about the latest cyber threats and follow the best practices for online security to minimize their risk of falling victim to cyber-attacks and protect their personal information. A well-informed worker (techie or not) will follow the best practices for password management.
To assist with this vital task, engage your employees in cybersecurity all year long with content branded for your company from Aware Force.
Check our Cybersecurity Newsletter page to get to know more or connect with us, and in 15 minutes, you’ll see why organizations across North America use cybersecurity content — branded for them — delivered by Aware Force.