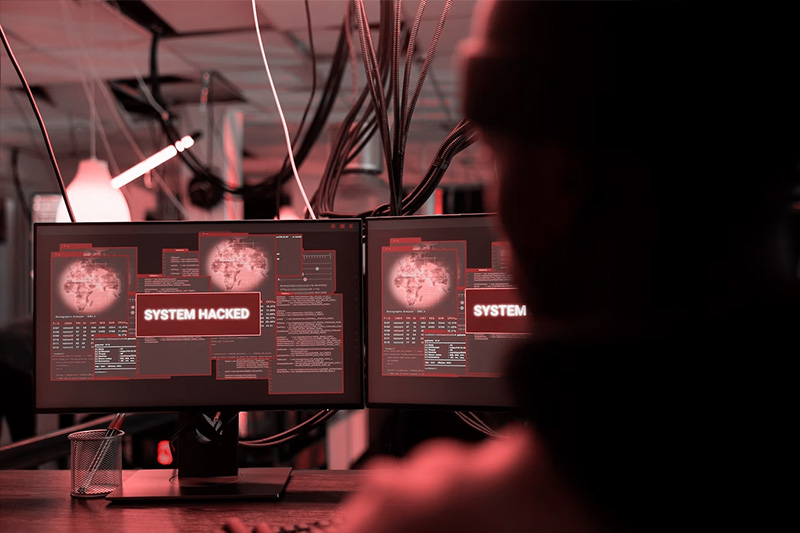
It looks like something out of a movie. But this is as real as it gets: the cautionary tale of how criminals exploited a patched vulnerability to deploy a man-in-the-middle attack to gain access to multiple databases of one of America’s biggest credit reporting agencies and steal the personal information of 147 million citizens.
This is a great case study. We’re including a brief recap on man-in-the-middle attacks, but you can skip to the meat and bones.
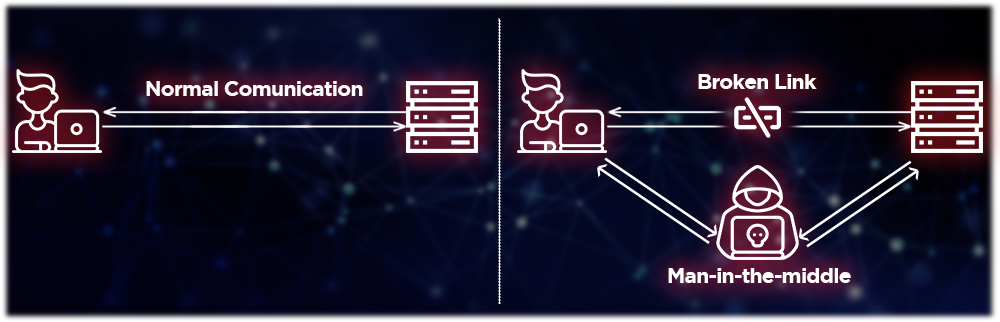
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) is a type of cyber attack in which an unauthorized party intercepts communication between two entities without their knowledge and insert themselves in the “middle” of the transfer. The attackers listen and manipulate information being exchanged, allowing them to steal information and send malicious links while remaining undetected.
It’s like a devious translator modifying conversation between two individuals who speak different languages.
MitM attacks are a type of session hijacking where hackers exploit real-time conversations or data transfers by breaking the original link and inserting themselves in the middle. There are different ways to implement such attacks, and here’s an example in 2 steps:
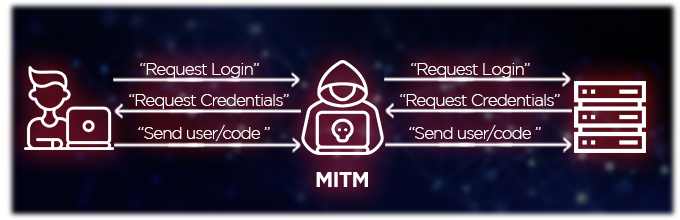
MITM attacks can be carried out in a variety of ways, but some of the most common methods include:


In 2017, the personal data of hundreds of millions of people was stolen from Equifax, one of the three big credit reporting agencies that assess the financial health of nearly adult in the US.
The origin of the Equifax crisis can be traced to March 2017 when a critical vulnerability, identified as CVE-2017-5638, emerged in the open-source web application framework Apache Struts. This framework, heavily embedded within Equifax’s operations, would become the initial infiltration point.
Note for CISOs: Patches for this vulnerability were available, but Equifax lagged in installing the security updates.
The attackers capitalized on the unpatched Struts vulnerability, initiating their assault via a consumer complaint web portal. But what transforms this from an intrusion to a man-in-the-middle attack is the subsequent deployment of a malicious Java application, masquerading as a legitimate Equifax tool. As customers interfaced with what they believed to be an authentic Equifax application, their data traffic was being intercepted and manipulated in real time, granting attackers unprecedented access to sensitive data.
Stolen data included consumers’ names, addresses, dates of birth, social security numbers, and credit card numbers.
Note for CISOs: The systems weren’t adequately segmented from one another, allowing the attackers to move from the infected web portal to multiple servers and databases.
In hindsight, Equifax’s response was riddled with questionable decisions. The six-week delay in disclosing the breach after its discovery is a reminder of the reputational ramifications of slow response strategies. But that was one of many missteps. Internally, Equifax missed crucial clues.
Note for CISOS: A CISO would immediately identify the absent security layers: unencrypted sensitive data, a lack of multi-factor authentication, and the delay in patching a known vulnerability.
While the immediate fallout of the breach centers around stolen personal information of over 147 million Americans, the damages went much further. The breach is a tale of technical vulnerabilities and exploitation and underscores systemic issues within the management of Credit Reporting Agencies (CRAs)
The Equifax breach is an alarming testament to how a seemingly minor technical oversight can spiral into a catastrophe. While the breach was facilitated by a failure to patch known software vulnerabilities, the subsequent mishandling further amplified its effects.
Ultimately, this breach cost Equifax over $700 million in damages, including the cost of investigation, fixing damages, and compensating customers.
Of course, the impact of such a breach extends way past the dollar signs:
MITM attacks prey on technical and human vulnerabilities. It’s a reminder that our network infrastructures are only as robust as the least informed employee with access.
While technical defenses like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and diligent patching are critical, an educated and vigilant workforce serves as a formidable first line of defense.
Here are a couple of things to reinforce with your team:
CISOs and cybersecurity teams are under tremendous pressure, often competing for qualified employees. While there are outstanding technical tools to test and track employees’ cybersecurity prowess, the key to engaging employees isn’t automation. It’s actionable videos, quizzes, infographics, the latest cyber news, and answers to common questions written in a style they can understand and share with their families.
It’s easy to use and cost-effective. And it’s branded and customized so all the content comes from the IT team. That’s the Aware Force business model that generates unsolicited praise from employees and fierce loyalty from our customers. Check out our extensive cyber library and our terrific twice-monthly cybersecurity newsletter — all branded for you.